Introduction

In this article, Dr Shree Rao talks about cochlear implant rehabilitation. She is the Best Doctor for Cochlear Implants.
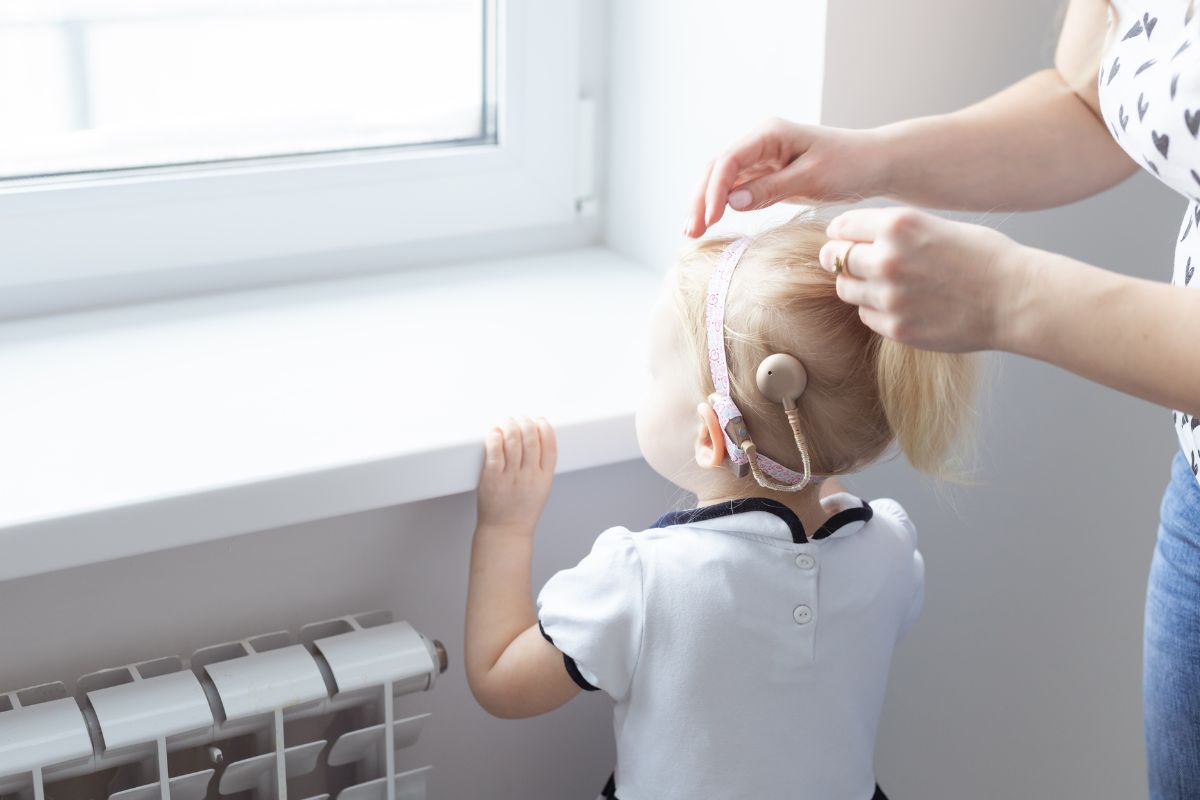
Cochlear implant rehabilitation is a life-changing process that offers renewed hope and possibilities for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss. This article delves into the deeper understanding of the transformative potential of cochlear implants and the invaluable support provided by a comprehensive rehabilitation program. By examining the significance of audiological assessments, speech and language therapy, auditory training, and the use of assistive devices, an individual can uncover the multifaceted approach taken to optimize the benefits of cochlear implants. This exploration of cochlear implant rehabilitation highlights the remarkable impact it has on an individual’s communication and overall quality of life.
Listening hierarchy
The listening hierarchy is a framework used in auditory rehabilitation for individuals with cochlear implants to develop their listening skills progressively. It encompasses various levels of auditory perception and comprehension. Here is an outline of the listening hierarchy:
- Environmental sounds – The first level involves recognizing and differentiating common environmental sounds, such as doorbells, telephone rings, or footsteps.
- Ling sounds – Ling sounds are specific speech sounds that cover a range of frequencies and are used to develop auditory perception. These include /m/, /a/, /u/, /i/, /s/, and /sh/. The individual learns to identify and discriminate these sounds.
- Syllables – This level focuses on perceiving and differentiating syllables, which are combinations of ling sounds. The individual practices listening to syllables and distinguishing between different combinations.
- Words – At this stage, the individual works on understanding and recognizing spoken words. He / she learns to identify common words and improve their word discrimination skills.
- Phrases and sentences – The next step involves comprehending phrases and sentences. The individual practices understanding longer utterances and extracting meaning from context.
- Conversational speech – The final level aims at achieving proficiency in understanding conversational speech. The individual develops their ability to follow conversations, participate actively, and comprehend spoken language in various real-life situations.
It’s important to note that progression through the listening hierarchy is individualized, and the pace of development may vary depending on the person’s specific circumstances and rehabilitation progress. Audiologists, speech-language pathologists, and cochlear implant rehabilitation specialists play a crucial role in guiding individuals through the listening hierarchy and tailoring interventions to their unique needs and abilities.
Auditory training and speech therapy
Auditory training and speech therapy are crucial components of rehabilitation following a cochlear implant. These interventions aim to optimize the individual’s ability to hear, understand, and communicate effectively. The following are some key aspects to consider in auditory training and speech therapy:
- Discrimination exercises – Training to differentiate between different speech sounds and environmental sounds.
- Auditory memory exercises – Enhancing the ability to remember and recall auditory information.
- Auditory closure activities – Practicing the comprehension of incomplete or partially masked speech.
- Speech sound identification – Focusing on accurately recognizing and reproducing speech sounds.
- Word and sentence-level practice – Building vocabulary and sentence structure to improve comprehension and expression.
- Articulation exercises – Targeting specific speech sounds or patterns to enhance clarity of speech.
- Vocabulary building – Expanding the individual’s vocabulary through exposure to new words and concepts.
- Syntax and grammar exercises – Working on sentence construction, word order, and grammatical rules.
- Pragmatic language skills – Developing social communication abilities, including turn-taking and maintaining conversations.
- Contextual cues – Utilizing visual cues, gestures, and facial expressions to aid in understanding spoken language.
- Communication repair techniques – Teaching strategies to clarify misunderstandings and ask for repetition or clarification.
- Conversational practice – Engaging in role-playing activities to improve conversational skills and interactions.
Training on the effective use of ALDs, such as FM systems or Bluetooth connectivity, to enhance hearing and communication in challenging listening environments.
The auditory training and speech therapy should be personalized to meet the individual’s specific needs and goals. Regular and consistent practice, along with ongoing support, can significantly contribute to the individual’s progress in auditory skills and communication abilities.
Development of listening and language skills
The development of listening and language skills depends on the following key areas:
- Auditory discrimination
- Auditory memory and sequencing
- Vocabulary building
- Syntax and grammar
- Auditory closure
- Pragmatic language skills
- Language comprehension and expression
Assistive listening devices and accessories
Some common assistive listening devices (ALDs) and accessories are:
- Personal amplifiers – Pocket-sized devices that amplify sound, making it easier to hear in various environments. They can be used with headphones or earbuds for personal use, or with a neckloop to connect to a hearing aid or cochlear implant.
- FM systems – They are wireless systems that transmit sound directly to a receiver worn by the individual. The speaker wears a microphone, and the sound is transmitted to the receiver, providing improved clarity and reduced background noise.
- Loop systems – Inductive loop systems use electromagnetic fields to transmit sound directly to hearing aids or cochlear implants. They are widely used in public spaces, such as theaters, conference rooms, and churches, where a looped wire is installed to create a listening loop.
- Bluetooth accessories – Wireless devices that connect to smartphones, TVs, and other audio sources to stream sound directly to hearing aids or cochlear implants. They enable hands-free phone calls, audio streaming, and direct connection to various electronic devices.
- TV listening systems – TV listening systems are devices that wirelessly transmit audio from a television to a receiver worn by the individual. They allow the user to adjust the volume to a comfortable level without disturbing others in the room.
- Telephone amplifiers and captioning devices – Amplifiers increase the volume of telephone conversations for individuals with hearing loss. While captioning devices display text captions of phone conversations in real-time.
- Remote microphones – Portable microphones that can be placed near a speaker to capture their voice and transmit it directly to the individual’s hearing aids or cochlear implants. They are useful in situations where there is distance or background noise, such as in classrooms, meetings, or social gatherings.
School and educational support

The following are some key aspects of school and educational support for cochlear implant rehabilitation:
- Individualized education plan (IEP) – The development of an Individualized education program (IEP) that collaboratively outlines goals, accommodations, and services for students with cochlear implants involves educators, audiologists, speech therapists, and parents working together to customize the educational experience.
- Classroom accommodations – To optimize auditory access and minimize background noise, students with cochlear implants benefit from utilizing assistive listening devices, such as FM systems or loop systems, as well as being provided with preferential seating near the teacher.
- Speech and language therapy – Regular therapy sessions with speech-language pathologists are essential in collaborating to improve speech production, language skills, auditory comprehension, and communication strategies for children with cochlear implants. Additionally, incorporating auditory training exercises helps strengthen listening skills and promote speech development.
- Teacher and staff training – Training sessions are conducted for teachers and school staff to increase awareness and understanding of cochlear implants, hearing loss, and effective strategies to support students. Open communication and collaboration between teachers, parents, and healthcare professionals are encouraged to ensure consistent support for the student.
- Peer support and inclusion – An inclusive and supportive environment is fostered by promoting the interaction and learning of students with cochlear implants alongside their peers, while also educating classmates about hearing loss and cochlear implants to cultivate empathy, understanding, and acceptance.
- Regular monitoring and assessment – Regular assessments are conducted to monitor the student’s progress in speech, language, and academics, with educational strategies and accommodations adjusted accordingly to meet evolving needs and optimize learning outcomes.
- Parent involvement and education – Parents are actively engaged in their child’s educational process, provided with resources and information to support their child’s cochlear implant rehabilitation, and encouraged to participate in IEP meetings, communicate with educators, and reinforce skills learned in school through home-based activities.
Rehabilitation for adults with cochlear implants
The rehabilitation process for adults involves a comprehensive approach tailored to individual needs and may include the following components:
- Auditory Training – Adults undergo auditory training programs to develop and refine their listening skills. These programs involve structured activities and exercises to improve speech perception, sound recognition, and discrimination.
- Speech Therapy – Speech therapy sessions focus on enhancing speech production and clarity. Professionals work with adults to improve articulation, intonation, and overall speech intelligibility.
- Language Development – Language therapy aims to improve language skills, including vocabulary, grammar, syntax, and comprehension. This may involve targeted exercises, conversation practice, and strategies to enhance communication in various settings.
- Counseling and Support – Rehabilitation includes counseling and support services to address the emotional and psychological aspects of living with a cochlear implant. This may involve discussions about adjusting to the implant, managing expectations, and coping with any challenges or concerns.
- Assistive Listening Devices – Adults with cochlear implants may benefit from using assistive listening devices such as personal FM systems, remote microphones, or Bluetooth accessories. These devices can enhance speech understanding in challenging listening environments, such as noisy or large group settings.
- Follow-up and Auditory Mapping – Regular follow-up appointments with audiologists are essential to fine-tune and adjust the cochlear implant’s settings for optimal performance. This process, known as auditory mapping or programming, ensures that the device is providing the most effective sound perception.
- Support Groups and Peer Networks – Engaging in support groups and connecting with other cochlear implant users can provide valuable emotional support, shared experiences, and practical tips for successful integration of the implant into daily life.

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!