Introduction - Understanding ear injuries in sports

In this article, Dr Shree Rao talks about ear injuries in sports. She is the Best Doctor for Cochlear Implants.
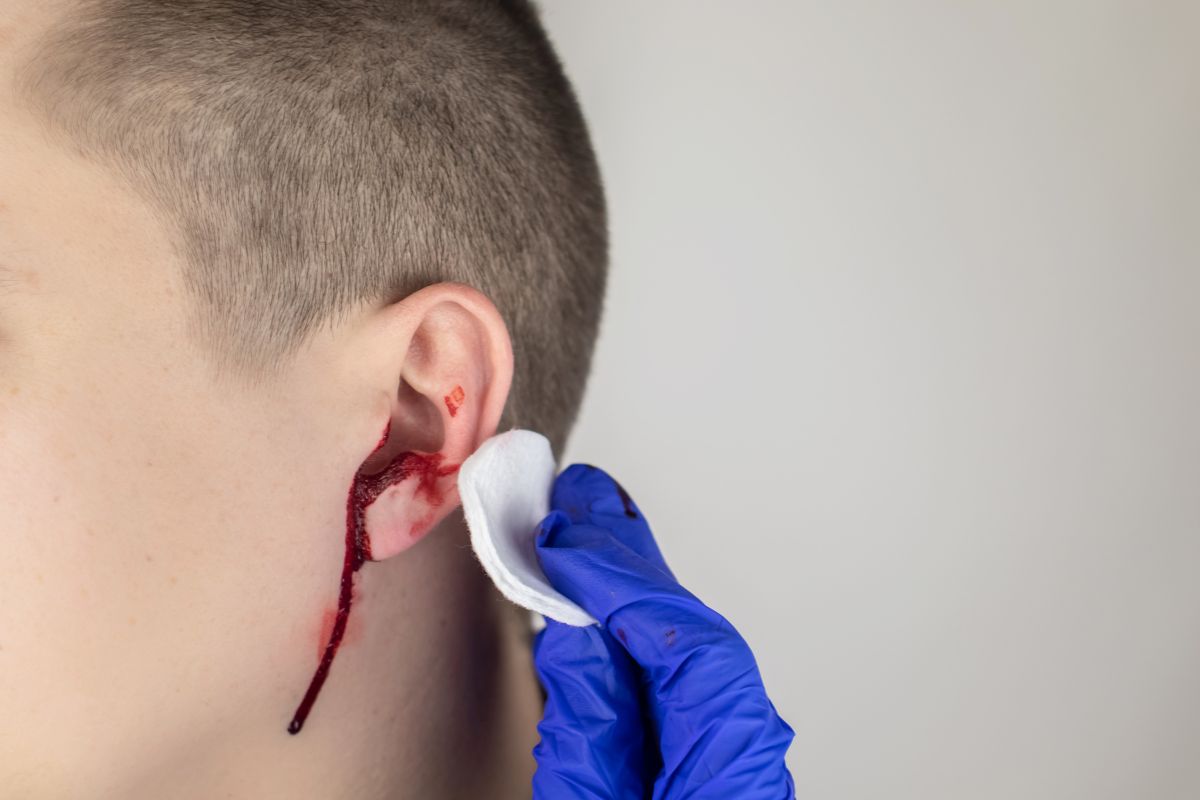
Ear injury, often overshadowed by more apparent sports injuries, is a significant concern in athletics. This blog delves into the world of ear trauma, exploring its impact on athletes. From the intricacies of ear anatomy to common types of injuries, it emphasizes prevention and timely intervention.
Athletes expose their ears to potential hazards during intense physical activities, leading to injuries like auricular hematomas and canal lacerations. Neglected injuries can result in chronic issues, affecting performance and quality of life. This blog underscores the importance of ear trauma awareness, advocating for protective gear, medical attention, and a culture of ear safety in sports.
Dr. Shree Rao’s expertise becomes a pivotal factor in the arena of ear trauma. With her proficiency in ear anatomy and trauma management, she stands as a dependable resource for athletes seeking comprehensive care. Through her patient-centered approach, Dr. Rao assists athletes in navigating the complexities of ear trauma, ensuring that their auditory well-being remains intact. By addressing injuries promptly and employing state-of-the-art interventions, she plays a vital role in safeguarding both short-term recovery and long-term ear health.
Anatomy of the ear and vulnerable areas
The human ear comprises several delicate structures responsible for both hearing and balance. While athletes engage in sports with determination and vigor, it’s essential to recognize the vulnerability of the ear’s anatomy to trauma. Understanding the specific areas prone to injury can lead to informed preventive measures and timely interventions. Here’s a breakdown of the ear’s anatomy and its vulnerable components in the context of sports:
- The pinna, or the visible outer part of the ear, is susceptible to direct impact, particularly in contact sports.
- Injuries to the pinna can result in contusions, hematomas, and abrasions, which may compromise aesthetics and function.
- The ear canal, a slender passage leading to the eardrum, is vulnerable to blunt force trauma and foreign object penetration.
- Inadequate protection can lead to ear canal lacerations, infections, and potential damage to the delicate eardrum.
- The eardrum separates the external ear from the middle ear and is integral for hearing.
- Direct impact or sudden changes in pressure can rupture the eardrum, causing hearing loss and susceptibility to infections.
- The ossicles (small bones) in the middle ear transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear.
- Forceful trauma can dislocate or fracture these bones, resulting in conductive hearing loss and other auditory issues.
- The inner ear houses the vestibular system, responsible for balance and spatial orientation.
- Trauma to the inner ear can lead to dizziness, vertigo, and imbalance, affecting an athlete’s performance and safety.
- The cochlea is the spiral-shaped structure responsible for converting sound vibrations into neural signals.
- Injuries to the cochlea can lead to sensorineural hearing loss, affecting an athlete’s auditory perception.
- Nerves controlling facial expressions pass through the ear and face.
- Trauma to these nerves can result in facial paralysis and related functional difficulties.
Common ear injuries in sports
In the realm of sports, where intense physical activities often coincide with dynamic movements, collisions, and swift changes in pressure, the risk of ear injuries is a notable concern. These injuries, while varied in nature, can significantly impact an athlete’s well-being and performance. Here’s a closer look at some of the frequently encountered ear injuries in the sporting arena:
- Auricular hematoma (Cauliflower ear)Auricular – Hematoma, or cauliflower ear, results from blood collecting between the outer ear’s cartilage and skin due to direct impacts or friction, prevalent in contact sports like wrestling and rugby. Left untreated, it distorts the ear’s shape and function.
- Ear canal lacerations – Ear canal lacerations, caused by trauma or foreign objects, result in tears or cuts in the ear canal lining. Factors include blunt force, accidental abrasions, or foreign objects. The outcomes can involve bleeding, infection risk, and temporary hearing impairment.
- Perforated eardrum – Perforated eardrum, a tear in the membrane separating the outer and middle ear, often results from pressure changes, trauma, or loud sounds. The consequences include reduced hearing, infection vulnerability, and possible vertigo. Middle ear trauma – Middle ear injuries, affecting structures like the sound-transmitting ossicles, often result from forceful collisions, like a blow to the head’s side. They lead to conditions like conductive hearing loss, disrupted sound propagation, and potential equilibrium problems.
- Inner ear injury – The inner ear, crucial for balance and spatial orientation, can be injured by sudden jolts or forceful head impacts. This can result in symptoms like dizziness, vertigo, impaired balance, and compromised spatial orientation.
- Barotrauma – Barotrauma is a unique injury caused by rapid pressure changes, common during activities like scuba diving. Inadequate pressure equalization between the middle and outer ear leads to issues such as ear pain, eardrum rupture, and potential effects on auditory and vestibular systems.
Recognizing ear injuries
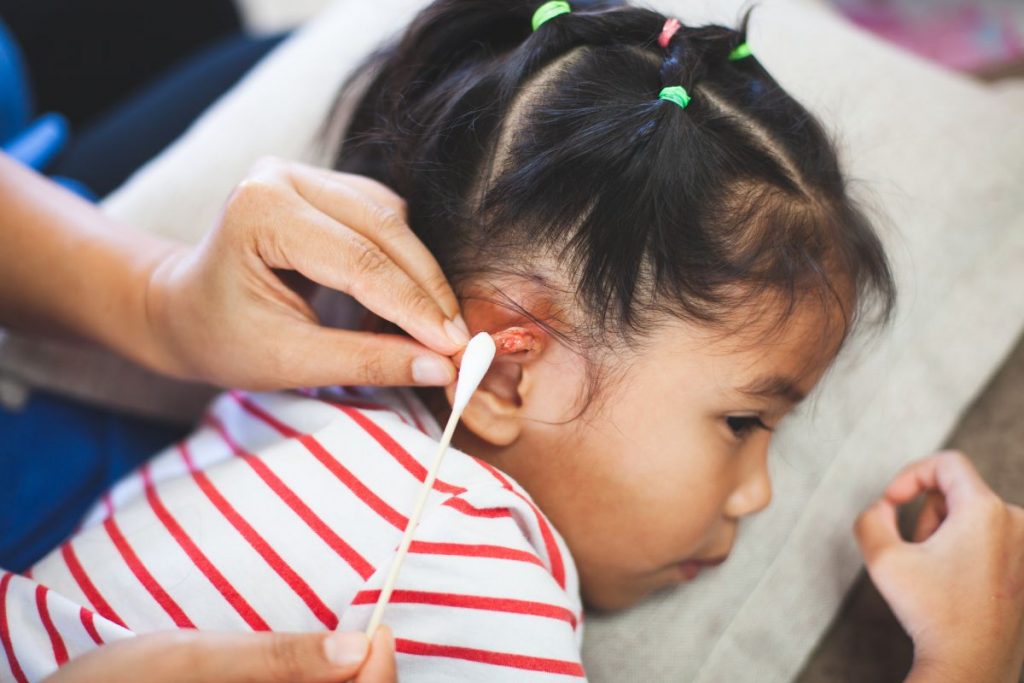

Here is a list of signs and symptoms commonly associated with ear injuries:
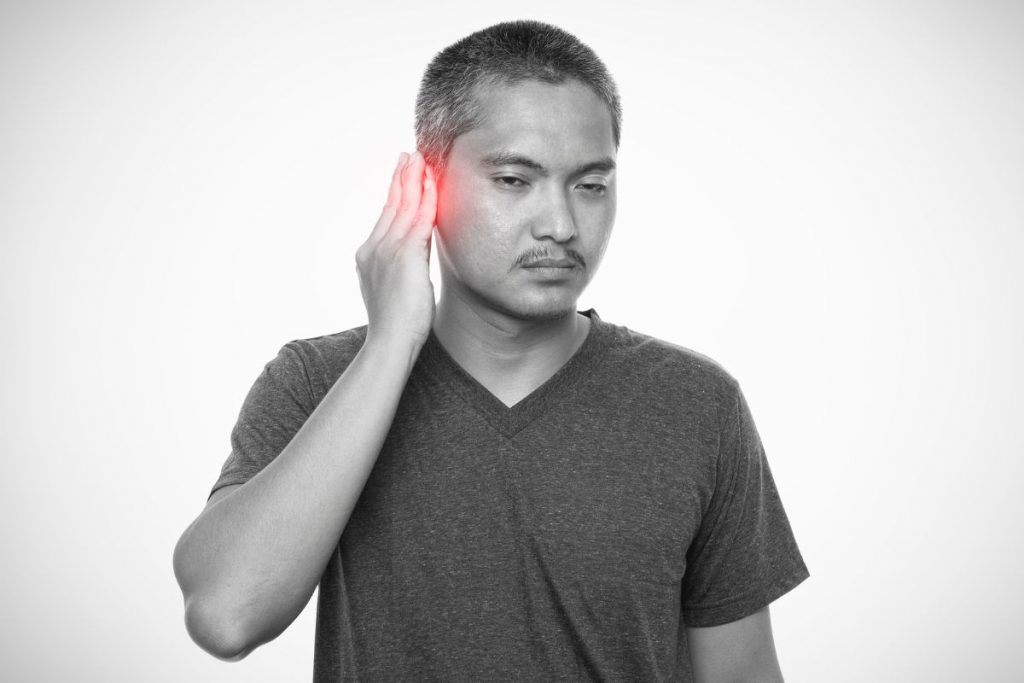
- Pain
- Itching
- Sense of pressure within the ear
- Bleeding
- Fluid discharge
- Diminished hearing
- Distorted hearing
- Vertigo
- Nausea or vomiting
- Swelling
- Deformity
- Ear canal pain
- Facial weakness or twitching
- Imbalance or unsteadiness
- Eardrum rupture
- Sensitivity to noise
- Earache
- Fever
Preventing ear injuries in sports
- Educate athletes about the importance and proper usage of protective gear.
- Ensure helmets fit well and meet quality standards.
- Consider customized ear protection for high-risk sports.
- Adhere to recommended headgear usage guidelines.
- Regularly inspect and maintain protective gear.
- Emphasize proper technique and body positioning.
- Create hazard-free playing environments.
Incorporate warm-up and stretching routines. - Launch educational campaigns on ear injury prevention.
- Prioritize immediate medical attention for suspected injuries.
- Follow prescribed recovery protocols and rehabilitation.
- Maintain hygiene and avoid shared equipment.
- Foster communication with medical professionals for guidance.
First aid for ear injuries
- Maintain a calm and composed atmosphere around the injured individual.
- Apply a clean cloth or sterile gauze to control bleeding from the outer ear.
- Refrain from inserting objects into the ear canal to avoid exacerbating the injury.
- Evaluate the injury’s severity and potential complications.
Gently cover the injured ear with a sterile cloth or dressing. - Advise the injured person to keep their head upright to minimize pressure changes.
- Caution against actions like forceful nose blowing that can worsen certain ear injuries.
- Promptly seek medical evaluation, even for seemingly minor injuries.
If eardrum perforation is suspected, prevent water exposure to the injured ear. - Document the injury circumstances for medical professionals.
Clearly communicate injury details to medical professionals. - Encourage minimal head and ear movement to prevent further injury.
Remember that while first aid measures can be valuable, seeking professional medical attention remains paramount for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of complications.
Treatment approaches for ear injuries
- Swift and thorough medical evaluation for injury assessment.
- Non-surgical management for minor injuries, including pain and antibiotic treatment.
- Surgical drainage of auricular hematomas to prevent deformities.
- Surgical interventions for severe injuries, fractures, and repairs.
- Surgical grafting (tympanoplasty) for perforated eardrums.
- Suturing or closure methods for ear canal lacerations.
- Surgical repair of dislocated or fractured middle ear ossicles.
- Customized vestibular rehabilitation to restore balance.
- Prescribed medications for infections resulting from injuries.
- Regular follow-up appointments to monitor healing progress.
- Adjusting activities to prevent strain during recovery.
- Education on protective gear and injury prevention.
Offering psychological support for coping with substantial injuries or hearing loss.
Long-term effects of untreated ear injuries
- Hearing impairment
- Balance and equilibrium disorders
- Chronic pain and discomfort
- Infections
- Psychological impact
- Communication challenges
- Reduced quality of life
Conclusion
In summation, the profound and lasting consequences of untreated ear injuries underscore the critical importance of prompt and comprehensive medical intervention. From enduring hearing impairment and balance disruptions to chronic discomfort and psychological distress, the effects of neglecting ear injuries can cast a wide shadow over an individual’s well-being and quality of life. Athletes, coaches, and medical professionals should recognize that these potential long-term outcomes are preventable through timely treatment and a commitment to preventive measures.
Athletes seeking to preserve their auditory health and overall well-being can trust Dr. Shree Rao’s guidance and commitment to delivering the highest standard of care. Through early intervention and adherence to treatment protocols, Dr. Shree Rao empowers individuals to navigate the trajectory of recovery, ensuring optimal outcomes and the restoration of a fulfilling, active lifestyle.

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!