Introduction to Hearing Test

In the discourse presented here, Dr. Shree Rao provides When to Consider Having a Hearing Test. She is the Best Doctor for Cochlear Implants.
Embarking on the journey of maintaining optimal auditory health requires a keen awareness of when to consider having a hearing test. In this comprehensive guide, readers will explore the crucial indicators and factors that prompt the need for a hearing assessment. Guided by a professional tone and expert insights, such as those provided by Dr. Shree Rao, readers will gain valuable knowledge about the significance of regular hearing evaluations in preserving hearing acuity and overall well-being.
1. Changes in Hearing Perception
Changes in hearing perception can be subtle at first but may indicate underlying issues that warrant attention. Individuals experiencing alterations in their ability to hear may notice several key indicators that signal a potential decline in auditory function.
Difficulty Understanding Conversations
Individuals facing challenges in understanding conversations, especially in noisy environments, may indicate a decline in their hearing perception. Struggling to follow discussions or asking for repetitions can be early signs of hearing difficulties that warrant attention and evaluation by a qualified audiologist.
Asking Others to Repeat Themselves
Frequent requests for repetition during interactions may signal difficulties in hearing clearly, potentially indicating a decline in hearing acuity. People noticing themselves asking others to repeat more often should consider seeking professional evaluation to address any underlying hearing issues.
Struggling to Hear Speech on the Phone
Difficulty understanding speech over the phone despite adequate volume settings may suggest changes in hearing perception. Challenges in discerning words or phrases during phone conversations can lead to communication difficulties, highlighting the need for further assessment.
Gradual Decrease in Auditory Clarity
A gradual decline in the clarity of sounds and speech perception over time may indicate changes in hearing perception. Individuals noticing muffled or less distinct sounds should consider seeking evaluation to address any underlying hearing issues and improve auditory experiences.
Sensitivity to Environmental Sounds
Increased sensitivity to loud or sudden sounds, or conversely, decreased awareness of softer sounds, may signal changes in hearing perception. Feeling uncomfortable or overwhelmed by certain sounds can affect individuals’ comfort in various environments, prompting the need for evaluation.
Inconsistent Responses to Auditory Stimuli
Inconsistencies in responding to auditory stimuli, such as failing to react to familiar sounds or overreacting to certain noises, may suggest changes in hearing perception. Observing variations in responses to sounds can provide valuable insights into individuals’ auditory function, necessitating further assessment.
Impact on Social Interactions
Changes in hearing perception can significantly impact social interactions and communication. Individuals experiencing difficulties may withdraw from social activities or avoid group settings due to challenges in hearing and understanding conversations, highlighting the need for professional evaluation and support.
Fatigue and Strain During Conversations
Increased fatigue or mental strain during conversations, especially in noisy environments, may indicate changes in hearing perception. Individuals finding it exhausting to concentrate on listening and understanding speech may benefit from seeking evaluation to address any underlying hearing issues.
Awareness of Changes in Hearing
Heightened awareness of changes in hearing perception, such as noticing differences in auditory experiences or feeling a decline in hearing abilities, should not be overlooked. Individuals recognizing changes should prioritize seeking evaluation by a qualified audiologist for comprehensive assessment and management to address any underlying issues effectively.
2. Ringing or Buzzing Sensation (Tinnitus)
Tinnitus, often described as a ringing, buzzing, or humming sensation in the ears, is a prevalent audiological condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. While not a disease itself, tinnitus can be a symptom of an underlying auditory or neurological issue. Individuals experiencing tinnitus may perceive sound in one or both ears, with the intensity ranging from mild to severe, and the sound being constant or intermittent.
Tinnitus can arise from various factors, including exposure to loud noise, age-related hearing loss (presbycusis), ear infections, earwax buildup, or underlying medical conditions such as Meniere’s disease or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. In some cases, tinnitus may be a side effect of certain medications or a result of head or neck injuries.
3. Age-Related Factors
Age-related factors play a significant role in influencing auditory health and function, with advancing age often associated with changes in hearing sensitivity, auditory processing, and communication abilities. While age-related hearing loss, known as presbycusis, is a common concern among older adults, various other age-related factors can impact overall auditory well-being.
Presbycusis
Gradual hearing loss with age, affecting high-frequency sounds and speech comprehension, often due to inner ear changes and genetic factors.
Cognitive Decline
Age-related changes in memory and attention, overlapping with hearing loss and affecting speech perception.
Degenerative Changes
Structural and functional alterations in the auditory system, leading to difficulties in noisy environments and speech processing.
Tinnitus
Common in older adults, characterized by ringing or buzzing sounds in the ears, influenced by cochlear damage and neural activity changes.
Comorbid Health Conditions
Conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes exacerbate hearing difficulties, affecting blood flow and auditory nerve function.
Environmental Factors
Cumulative exposure to noise and ototoxic substances accelerates age-related hearing changes, necessitating protective measures.
4. Occupational Exposures
Occupational exposures pose significant risks to auditory health, with prolonged exposure to loud noise being a primary concern. Key aspects include:
Long-term exposure to high noise levels in workplaces such as construction sites, factories, and entertainment venues can lead to NIHL. This condition results from damage to the hair cells in the inner ear due to excessive noise exposure.
Exposure to ototoxic chemicals, including solvents, heavy metals, and certain medications, can damage the auditory system. These substances may disrupt the functioning of the cochlea or auditory nerve, leading to hearing loss or tinnitus.
Vibrations from machinery or equipment in industrial settings can cause damage to the inner ear structures over time. Prolonged exposure to vibrations may result in sensorineural hearing loss or exacerbate existing hearing conditions.
The effects of occupational exposures on auditory health are often cumulative, meaning that damage accrues gradually over time. Even intermittent exposure to loud noise or ototoxic substances can contribute to long-term hearing impairment.
5. Medical History
A comprehensive consideration of an individual’s medical history is crucial in determining when to consider having a hearing test. Factors such as chronic health conditions, medication usage, family history of hearing loss, previous noise exposure, age-related changes, and symptoms of hearing loss all play a significant role. Chronic health conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease, as well as certain medications, can impact auditory function. Additionally, a family history of hearing loss may increase susceptibility to auditory issues. Past exposure to loud noises, whether in work or recreational environments, can contribute to hearing damage over time. Age-related changes in hearing sensitivity and symptoms like difficulty understanding conversations or ringing in the ears should also prompt consideration of a hearing test. Overall, being proactive in monitoring auditory health through regular testing is essential for early detection and appropriate management of any potential hearing issues.
6. Impact on Daily Activities
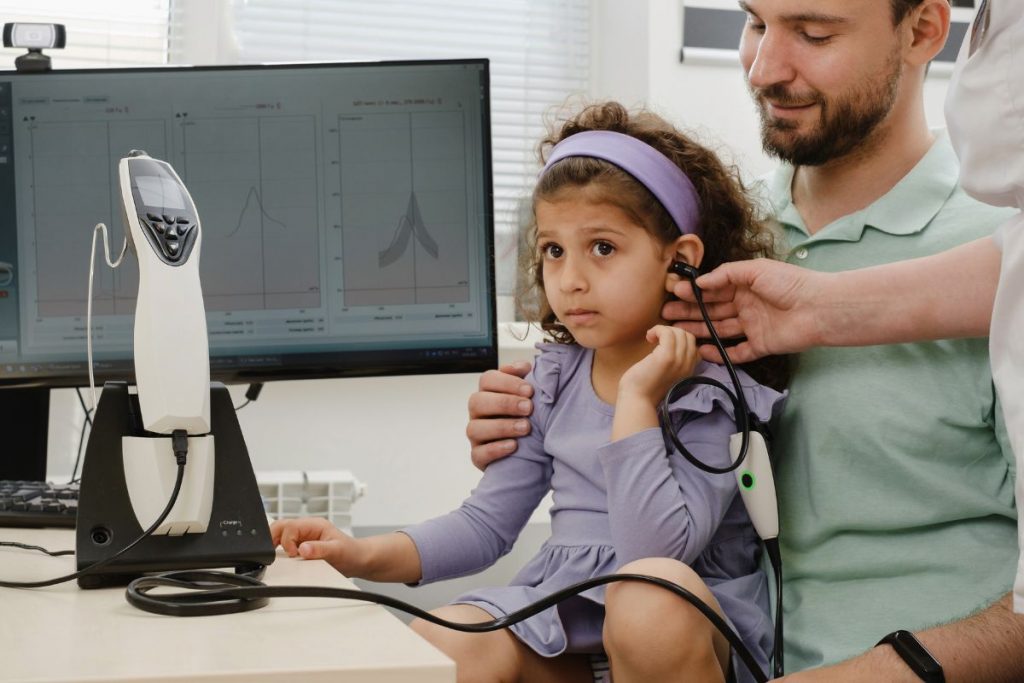
The impact of hearing loss on daily activities can be profound, affecting various aspects of an individual’s life. In professional settings, difficulty understanding conversations and instructions can hinder productivity and communication with colleagues. Simple tasks like answering phone calls or participating in meetings may become challenging, leading to frustration and decreased job performance. In social situations, hearing loss can isolate individuals, making it difficult to engage in conversations or enjoy social gatherings. Strained communication may result in feelings of embarrassment or withdrawal from social interactions. Additionally, hearing loss can affect personal relationships, as misunderstandings and miscommunication may arise with friends and family members. In leisure activities, such as watching television or listening to music, reduced hearing acuity can diminish enjoyment and limit participation. Overall, the impact of hearing loss on daily activities underscores the importance of seeking timely intervention and support to maintain a high quality of life.
7. Struggles with Speech Perception
Struggles with speech perception can significantly impact an individual’s ability to comprehend verbal communication effectively. This difficulty may manifest in various ways, including:
- Misunderstanding or misinterpreting spoken words or phrases, especially in noisy environments or during rapid conversations.
- Difficulty distinguishing between similar-sounding words or sounds, leading to confusion in understanding the intended message.
- Challenges in following conversations, particularly when multiple speakers are involved or when the speaker’s voice is distant or muffled.
- Inability to discern speech sounds or phonetic cues, resulting in incomplete or inaccurate comprehension of spoken language.
- Frustration or fatigue during prolonged conversations due to the cognitive effort required to process speech and extract meaning from auditory input.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the importance of scheduling a hearing test is essential for maintaining auditory health and overall well-being. Through this guide, individuals have gained valuable insights into the indicators and factors that signal the need for a hearing assessment. With expert guidance, such as that provided by Dr. Shree Rao, readers are empowered to take proactive steps towards addressing potential hearing concerns and ensuring optimal hearing acuity for years to come.

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!