Introduction - Understanding how colds and flu affect one's ears
In the discourse presented here, Dr. Shree Rao provides insights into comprehending the impact of colds and flu on ear health, coupled with indispensable ear care tips. She is the Best Doctor for Cochlear Implants.
In the world of respiratory infections, the effects of colds and flu extend beyond the common symptoms of coughing, sneezing, and congestion. An often-overlooked aspect of these illnesses is their impact on the ears. Understanding how colds and flu can affect the ears is essential, as it allows individuals to recognize the signs and take appropriate measures for ear health. Some of the viral infections and their influence on the ears are:
Ear congestion and pressure:
During colds and flu, individuals may experience ear congestion and a sensation of fullness or pressure. This occurs due to the interconnectedness of the ear, nose, and throat. Congestion in the nasal passages can extend to the Eustachian tubes, affecting ear pressure.
Otitis media:
Otitis media, commonly known as an ear infection, can be a complication of colds and flu. Viral upper respiratory infections can lead to inflammation of the middle ear, resulting in ear pain, fluid buildup, and sometimes even temporary hearing loss.
Impact on hearing:
In cases where otitis media develops as a complication, hearing may be affected. The presence of fluid or infection in the middle ear can impede sound transmission, leading to temporary hearing impairment.
Tinnitus:
Some individuals with colds or flu may experience tinnitus, a condition characterized by ringing, buzzing, or other noises in the ears. While this is usually temporary, it can be bothersome.
As the climate undergoes transformations and upper respiratory ailments become more prevalent, a discerning comprehension of how to preserve ear health is of immense value. In the expert care of professionals like Dr. Shree Rao, individuals can confidently navigate this season, assured that their auditory health is under the guidance of a capable specialist.
Proper hygiene and ear care tips to prevent ear infections
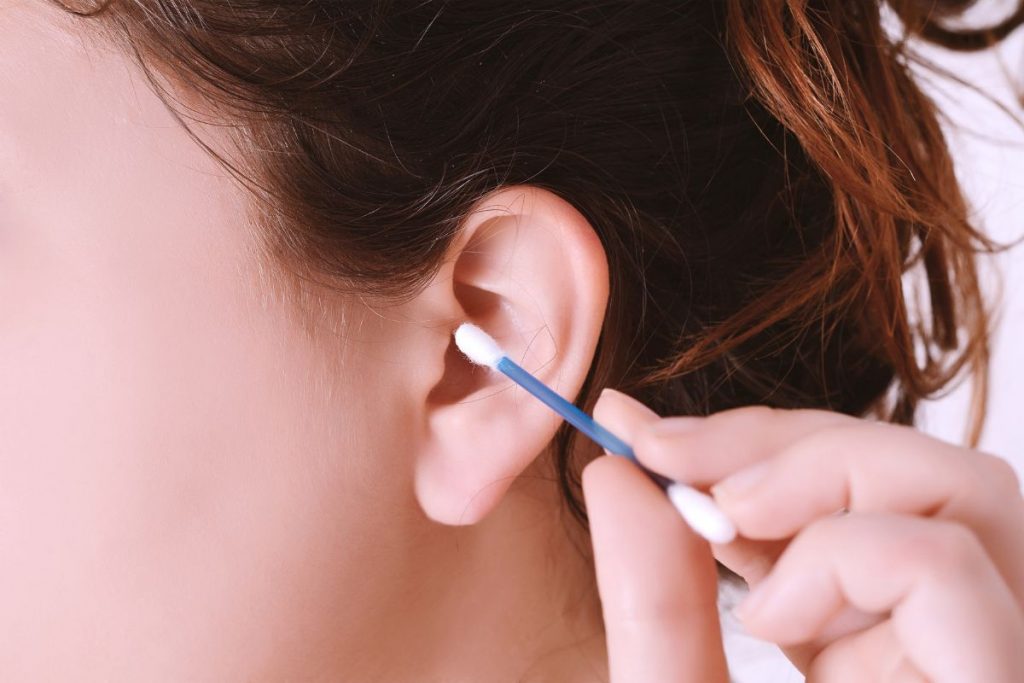

Ear cleaning:
When cleaning the ears, individuals should exercise caution. Avoid inserting cotton swabs or other objects into the ear canal, as this can push earwax deeper, potentially causing impaction or injury. Instead, clean the outer ear with a soft, damp cloth.
Ear protection:
In environments with loud noises, such as industrial settings or concerts, wearing hearing protection (earplugs or earmuffs) is essential to prevent noise-induced hearing loss and protect against potential infections.
Swimming precautions:
Swimmers should take precautions to prevent swimmer’s ear, a common ear infection. After swimming, tilt the head to allow water to drain from the ear and use a towel to dry the ears gently.
Earplugs for swimming:
Using specialized earplugs for swimming can create a barrier against water and moisture, reducing the risk of swimmer’s ear.
Avoiding excessive moisture:
Prolonged exposure to moisture in the ear can create a conducive environment for infections. After bathing, showering, or swimming, ensure the ear is adequately dried.
Respiratory hygiene:
Proper respiratory hygiene, including covering the mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing, can prevent the spread of respiratory infections that might lead to ear infections.
Avoiding allergens:
Allergies can contribute to ear infections. Minimize exposure to allergens and employ allergy management measures as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Seeking prompt treatment:
If an ear infection or ear-related symptoms such as pain, drainage, or hearing changes occur, it is crucial to seek prompt medical evaluation and treatment. Timely intervention can prevent the infection from worsening.
Regular check-ups:
Routine ear health check-ups with a healthcare professional are advisable to monitor and address any potential issues proactively.
Hearing protection:
When involved in activities where noise exposure is a concern, using hearing protection is vital to prevent noise-induced hearing damage, which can increase the susceptibility to ear infections.
Effective ear pain management
Warm compress:
Applying a warm, not hot, compress to the affected ear can help alleviate pain by improving blood circulation and reducing pressure. Ensure that the compress is not too hot to avoid burns.
Over-the-counter pain relievers:
Non-prescription pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can be effective in reducing ear pain. Follow dosing instructions carefully and consult a healthcare professional if uncertain.
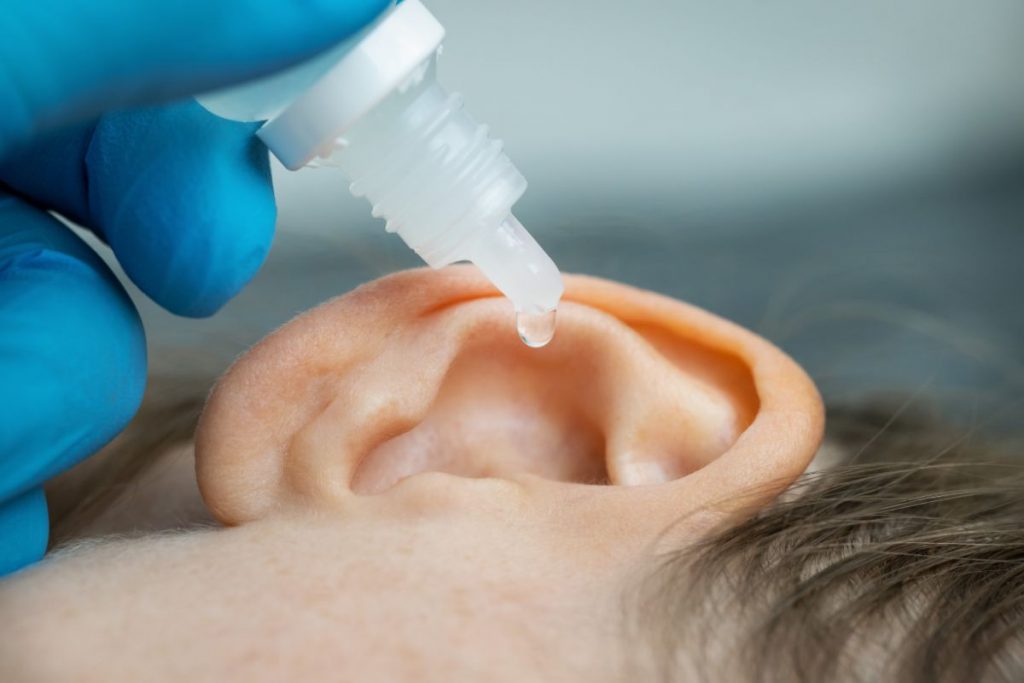
Ear drops:
Over-the-counter ear drops can provide relief for mild ear pain associated with conditions like swimmer’s ear. Ensure that the eardrum is intact before using ear drops and follow the package instructions.
Avoid inserting objects:
It is crucial not to insert objects, such as cotton swabs or fingers, into the ear canal, as this can exacerbate the problem and potentially lead to injury or infection.
Nasal decongestants:
If ear pain is due to congestion in the Eustachian tube, a nasal decongestant may help relieve the pressure. Consult a healthcare professional before use, especially for prolonged usage.
Avoid smoking:
Smoking can exacerbate ear pain and slow the healing process. It is advisable to avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
Recognizing when to seek professional ear care
If ear pain is severe, persists for an extended period, or worsens despite home remedies, it is prudent to consult a healthcare professional. This may indicate an ear infection or another underlying issue.
Any sudden or significant changes in hearing should prompt a visit to a healthcare professional, as this can be indicative of ear-related complications.
The presence of discharge or fluid coming from the ear is a clear sign that professional evaluation is needed. This may suggest an ear infection or perforation of the eardrum.
If the ears feel constantly full or under pressure, particularly during or after colds and flu, it can be a sign of Eustachian tube dysfunction or ear infection, necessitating professional examination.
If ear symptoms are accompanied by fever, chills, dizziness, or other systemic signs, this can indicate a more serious condition, and professional care is essential.
When ear-related symptoms persist or worsen after recovery from a cold or flu, it may signal a secondary ear infection or complication requiring professional attention.
Ear care tips for children during cold and flu season
Hand hygiene:
Teaching children proper handwashing techniques is the first line of defense against colds and flu, which can indirectly affect ear health. Encourage regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before meals and after coughing or sneezing.
Respiratory hygiene:
Instruct children to cover their mouths and noses when coughing or sneezing, using tissues or their elbows. This prevents the spread of germs that can lead to ear infections.
Avoiding close contact:
Educate children on the importance of maintaining a safe distance from those who are unwell to minimize the risk of respiratory infections.
Vaccinations:
Ensure that children receive recommended vaccinations, including the flu vaccine. Vaccination can significantly reduce the likelihood of contracting the flu, which can lead to complications affecting the ears.
Proper ear cleaning:
Emphasize gentle ear hygiene. Instruct children not to insert objects into their ears and to clean only the external ear with a soft, damp cloth.
Swimmer’s ear prevention:
If swimming is part of your child’s cold and flu season activities, ensure that they dry their ears thoroughly after swimming to prevent swimmer’s ear. Earplugs specifically designed for swimming can offer protection.
Preventing ear pressure:
During air travel or changes in altitude, teach children how to relieve ear pressure by swallowing, yawning, or sipping water.
Preventing the spread of illness to others
Respiratory hygiene:
Individuals should practice good respiratory hygiene by covering their mouths and noses with tissues or their elbows when coughing or sneezing. This prevents respiratory droplets, which can contain infectious agents, from becoming airborne.
Handwashing:
Regular and thorough handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds is a fundamental practice in preventing the spread of illnesses. Hand hygiene is especially crucial after coughing, sneezing, using the restroom, or before handling food.
Hand sanitizers:
When soap and water are unavailable, alcohol-based hand sanitizers with at least 60% alcohol content can be effective in disinfecting hands. However, they should not be considered a substitute for handwashing.
Avoiding close contact:
Individuals with symptoms of illness, such as fever, cough, or congestion, should avoid close contact with others, especially in crowded places. This reduces the risk of transmitting infections.
Face masks:
Wearing face masks can be effective in preventing the spread of respiratory illnesses, particularly in situations where physical distancing is challenging. Follow local guidelines and recommendations.
Cleaning and disinfecting:
High-touch surfaces in homes and public spaces, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops, should be regularly cleaned and disinfected to minimize the survival of viruses and bacteria.
Flu vaccination:
Receiving an annual flu vaccination is an important step in preventing the spread of seasonal influenza. This not only protects individuals but also reduces the risk of transmission.
Sick leave:
Encourage individuals to take sick leave when unwell, ensuring they have time to recover and reducing the risk of spreading illness to colleagues or peers.
Responsible cough etiquette:
Teach individuals to cough or sneeze into tissues or their elbows, and to dispose of tissues properly, to prevent contamination.
Conclusion
Preserving optimal ear health throughout the cold and flu season remains crucial. These actionable guidelines significantly diminish the likelihood of ear infections and associated complications. Understanding the pivotal role of healthy ears in maintaining overall well-being is key. Dr. Shree Rao is readily available to offer her expertise and attentive care. With an unwavering dedication to your ear health, you can confidently embrace the evolving seasons and relish the symphony of sounds that surround you.

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!