Introduction to Earlobe Gauging
In the discourse presented here, Dr. Shree Rao provides information about Earlobe Gauging: Complications, Consequences, and Correction. She is the Best Doctor for Cochlear Implants.
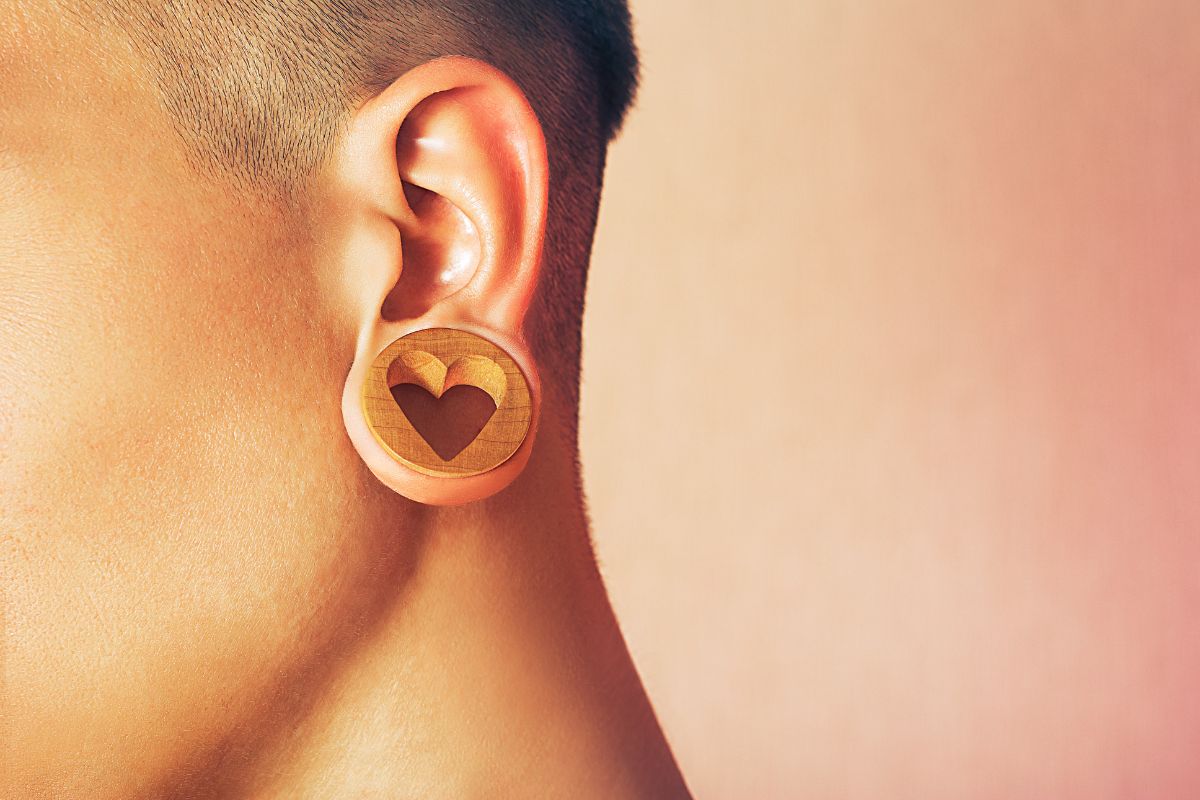
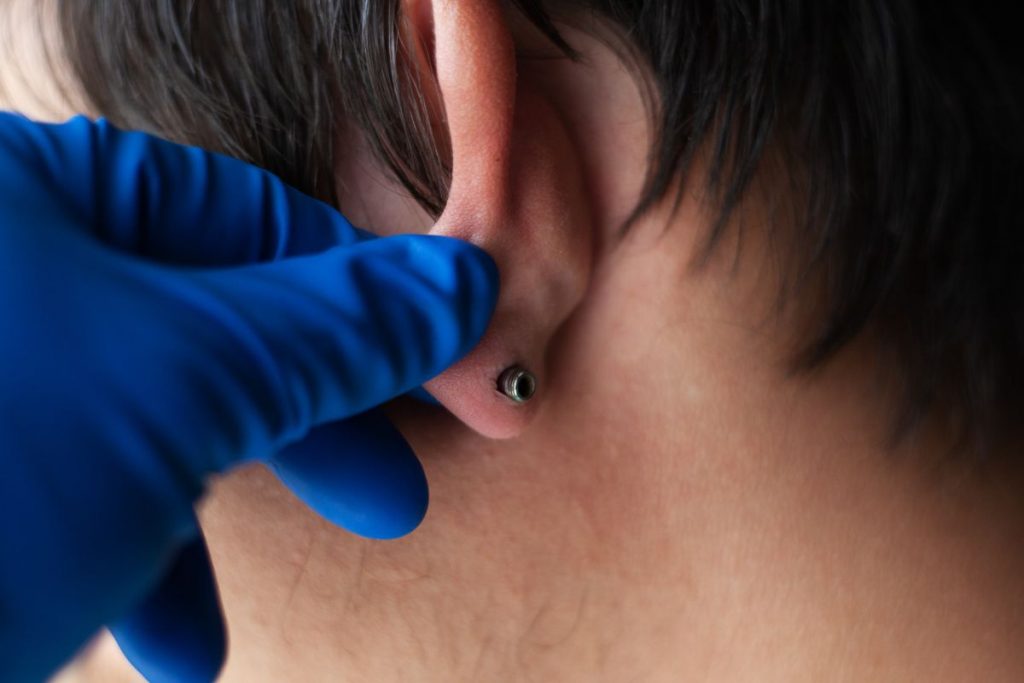
Earlobe gauging, also known as ear stretching or earlobe stretching, is a form of body modification that involves enlarging the earlobe piercing to accommodate larger jewelry. This practice has been around for centuries and holds cultural significance in various communities around the world. In recent years, earlobe gauging has gained popularity as a fashion statement and a means of self-expression.
The process of earlobe gauging typically begins with a standard ear piercing, which is gradually stretched over time using increasingly larger gauges or plugs. This stretching can be done manually or with the assistance of tapering tools designed for this purpose. As the earlobe gradually stretches, larger pieces of jewelry, such as plugs, tunnels, or tapers, can be inserted to create the desired look.
While earlobe gauging is often associated with younger generations and alternative subcultures, it has become increasingly mainstream and accepted in contemporary society. Many individuals choose to gauge their earlobes as a form of personal style or to make a statement about their identity.
However, it’s essential to approach earlobe gauging with caution and mindfulness of potential risks and considerations. Improper stretching techniques or using inappropriate jewelry sizes can lead to complications such as tearing of the earlobe, infection, or permanent stretching of the tissue. Therefore, it’s crucial to research proper gauging techniques, consult with experienced piercers or body modification professionals, and prioritize ear health and safety throughout the process.
Dr. Shree Rao’s expertise underscores the importance of informed decision-making and safe practices in earlobe gauging, ensuring a positive and healthy experience for enthusiasts.
Types of Earlobe Gauging
There are several methods and styles of earlobe gauging, each with its unique characteristics and considerations.
Tapering: Tapering involves inserting a tapered, conical-shaped device, known as a taper, into the existing earlobe piercing. The taper gradually widens the piercing as it is pushed through, stretching the surrounding tissue. Once the taper is fully inserted, jewelry of the desired size can be placed in the stretched piercing.
Taping: Taping, also referred to as bondage tape or PTFE tape method, involves wrapping layers of non-adhesive tape, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or bondage tape, around the existing jewelry. With each layer of tape added, the diameter of the jewelry increases slightly, gradually stretching the earlobe piercing over time.
Dead Stretching: Dead stretching, or natural stretching, involves allowing the earlobe piercings to gradually enlarge on their own over time without the use of external devices or tools. This method relies on the elasticity of the skin and the weight of the jewelry to stretch the piercing gradually. Dead stretching is typically a slower process compared to tapering or taping but may be preferred by individuals who wish to avoid discomfort or potential complications associated with more aggressive stretching methods.
Scalpelling: Scalpelling, also known as dermal punching, is a more invasive method of earlobe gauging that involves using a scalpel or dermal punch to create a larger hole in the earlobe. This method allows for rapid stretching of the earlobe piercing to accommodate larger gauge jewelry. Scalpelling is often performed by professional body modification artists and may be preferred for individuals seeking immediate or dramatic results.
Transdermal Implants: Transdermal implants involve surgically implanting a small anchor or disk beneath the skin to support larger gauge jewelry. This method is more invasive than traditional earlobe gauging techniques and carries a higher risk of complications, including infection and implant rejection. Transdermal implants are typically reserved for individuals seeking extreme modifications and should be performed by experienced professionals.
Complications of Earlobe Gauging
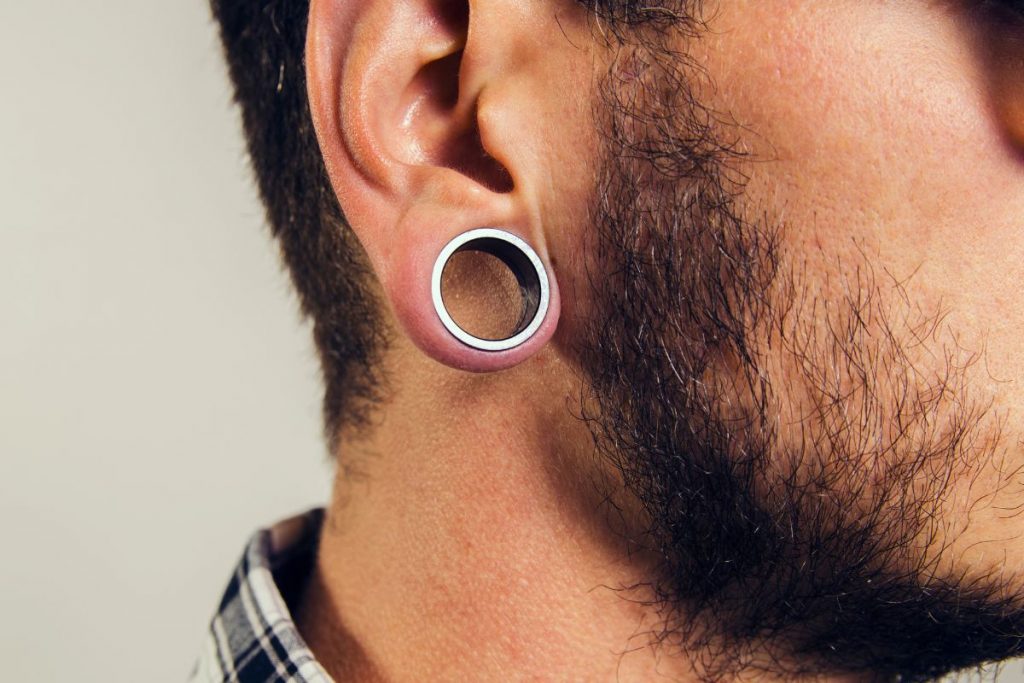

Here are some common complications associated with earlobe gauging:
Tearing or Blowouts: One of the most significant risks of earlobe gauging is tearing or blowouts, where the tissue surrounding the piercing is stretched beyond its elastic limit, resulting in a tear or rupture. This can lead to unsightly scarring, loss of tissue, and difficulty in further stretching or correcting the earlobe.
Infection: Earlobe gauging increases the risk of infection, especially if proper hygiene practices are not followed. Bacteria can enter the stretched piercing, leading to symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, and discharge. In severe cases, untreated infections can result in abscess formation and systemic illness.
Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: Some individuals are prone to developing keloids or hypertrophic scars, which are raised, thickened areas of scar tissue that form at the site of the stretched piercing. Keloids can be itchy, painful, and cosmetically displeasing, requiring medical intervention for management.
Migration and Rejection: In some cases, the body may recognize the stretched jewelry as a foreign object and attempt to push it out through a process known as rejection. This can result in migration of the jewelry, where it shifts or moves within the earlobe, causing discomfort and distortion of the piercing.
Nerve Damage: Aggressive stretching or improper technique can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation in the earlobe or surrounding areas. Nerve damage may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of injury and promptness of treatment.
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to the materials used in jewelry, such as nickel or certain metals. Allergic reactions can manifest as itching, redness, rash, or swelling at the site of the piercing, necessitating removal of the offending jewelry and avoidance of allergens.
Cosmetic Disfigurement: Complications such as tearing, scarring, or asymmetrical stretching can result in cosmetic disfigurement of the earlobe. This can have a significant impact on self-esteem and body image, prompting individuals to seek corrective procedures or camouflage techniques.
Functional Impairment: Severe complications of earlobe gauging, such as extensive scarring or tissue loss, can impair the function of the earlobe, affecting its ability to support jewelry or earrings. Functional impairment may require surgical intervention to restore normal anatomy and function.
Consequences of Earlobe Gauging
Here are some consequences of earlobe gauging:
Permanent Changes to Earlobe Anatomy: One of the most significant consequences of earlobe gauging is the permanent alteration of the earlobe anatomy. As the earlobe is stretched to accommodate larger gauges, the elasticity of the skin and underlying tissue is compromised, resulting in irreversible changes in shape, size, and texture.
Reduced Elasticity of Earlobes: Over time, repeated stretching of the earlobes can lead to a loss of elasticity in the skin and tissue, making it difficult for the earlobes to return to their original size or shape. This reduced elasticity can affect the ability to wear traditional earrings or may necessitate surgical correction to restore normal anatomy.
Social and Professional Implications: Earlobe gauging may have social and professional implications, as some individuals may perceive stretched earlobes as unprofessional or socially unacceptable. In certain industries or cultural settings, visible body modifications like earlobe gauging may impact perceptions of professionalism, credibility, or suitability for employment.
Difficulty in Reversal: While earlobe stretching is reversible to some extent, returning the earlobes to their pre-gauged state may be challenging or impossible, especially in cases of extensive stretching or tissue damage. Individuals who wish to reverse earlobe gauging may require surgical procedures such as earlobe reconstruction or cosmetic correction.
Increased Risk of Infection and Injury: Stretched piercings are more prone to infection and injury compared to standard earlobe piercings. The larger surface area exposed by stretched earlobes provides a breeding ground for bacteria and other pathogens, increasing the risk of localized infections, abscesses, and tissue damage.
Potential for Emotional Distress: Individuals who undergo earlobe gauging may experience emotional distress or dissatisfaction with their appearance, especially if they encounter complications such as tearing, scarring, or asymmetrical stretching. Cosmetic concerns or negative reactions from others may impact self-esteem, body image, and psychological well-being.
Cultural and Personal Identity Considerations: Earlobe gauging is often associated with cultural or personal identity markers and may hold significant symbolic meaning for individuals. However, it is essential to consider how earlobe gauging may be perceived within different cultural contexts and whether it aligns with personal values, beliefs, or goals.
Long-Term Maintenance and Care: Stretched earlobes require ongoing maintenance and care to prevent complications such as infection, tearing, or migration of jewelry. Individuals must adhere to strict hygiene practices, avoid trauma or pressure on the stretched piercings, and monitor for signs of inflammation or injury.
Correction Procedures for Earlobe Gauging
Individuals who wish to reverse earlobe gauging or address complications associated with stretched earlobes may consider the following correction procedures:
Surgical earlobe reconstruction is a common method used to repair stretched or damaged earlobes and restore their natural contour. During the procedure, a plastic surgeon or dermatologist carefully excises the excess tissue and reshapes the earlobe to achieve symmetry and proportion. Depending on the extent of stretching and tissue loss, techniques such as wedge excision, Z-plasty, or flap reconstruction may be utilized to achieve optimal results.
In cases of mild to moderate earlobe stretching, excision and primary closure may be sufficient to correct the deformity and reduce the size of the earlobe piercing. This procedure involves removing the stretched tissue along the length of the earlobe and suturing the edges together to create a smaller, more natural-looking earlobe shape. Excision and primary closure are typically performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis, with minimal downtime and scarring.
Earlobe reduction surgery, also known as earlobe reduction or earlobe reshaping, is a cosmetic procedure designed to improve the appearance of elongated or sagging earlobes. During the surgery, excess skin and tissue are excised from the lower portion of the earlobe to create a more youthful and proportionate contour. Earlobe reduction surgery can be performed as a standalone procedure or combined with other aesthetic enhancements, such as earlobe piercing repair or facelift surgery.
Tissue expansion techniques involve gradually stretching the skin and underlying tissue surrounding the earlobe to create additional tissue for reconstruction. This method is particularly useful in cases where significant tissue loss or scarring has occurred due to earlobe gauging or trauma. Tissue expanders, which are inflatable devices placed beneath the skin, are progressively inflated over several weeks to stimulate tissue growth and expansion. Once adequate tissue expansion is achieved, the expanders are removed, and the excess tissue is used to reconstruct the earlobe.
Injectable fillers and fat grafting procedures can be used to augment and reshape the earlobes, improving their volume, contour, and texture. Hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers or autologous fat harvested from the patient’s own body can be injected into the earlobe to restore lost volume and soften the appearance of wrinkles or depressions. These minimally invasive techniques offer temporary or long-lasting results, depending on the type of filler used and individual patient factors.
Non-surgical earlobe repair techniques, such as earlobe glue or adhesive strips, may be employed to temporarily close or conceal stretched earlobe piercings. While these methods are not permanent solutions, they can provide a quick and inexpensive alternative for individuals seeking to hide stretched piercings for special occasions or professional settings. Non-surgical earlobe repair options are often used as a temporary measure while planning for definitive correction procedures.
Scar revision and camouflage techniques may be utilized to minimize the appearance of scars or irregularities resulting from earlobe gauging or corrective surgery. Laser therapy, microneedling, dermabrasion, and topical scar creams are among the treatments available to improve skin texture, color, and tone and enhance the overall aesthetic outcome of earlobe repair procedures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while earlobe gauging offers a unique form of self-expression, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential complications and seek guidance from professionals like Dr. Shree Rao. With proper care and attention to ear health, individuals can minimize risks and enjoy the aesthetic benefits safely.

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!