Introduction
Mastoiditis is a condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. It can result from untreated middle ear infections and can have serious complications if not promptly managed. Understanding the definition and significance of mastoiditis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In this article, Dr Shree Rao talks about how you can get relief with mastoiditis treatment.
Anatomy and Function of the Mastoid Bone
The mastoid bone is a part of the skull located behind the ear, and it contains air cells that help regulate ear pressure. It plays a role in the anatomy of the ear and its surrounding structures, and understanding its location and structure is essential in comprehending mastoiditis and its potential complications.
Causes of Mastoiditis
Mastoiditis is commonly associated with middle ear infections, particularly when they are not adequately treated. Bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, are often responsible for mastoiditis. Risk factors for mastoiditis include age (children are more susceptible), a weakened immune system, and a history of recurrent ear infections.
Symptoms of Mastoiditis
Symptoms of mastoiditis may include severe ear pain, fever, redness, swelling, and tenderness behind the ear. Other possible symptoms include drainage from the ear, hearing loss, and a general feeling of illness. Recognizing the common symptoms of mastoiditis is important in early detection and appropriate management of the condition.
Diagnosis of Mastoiditis
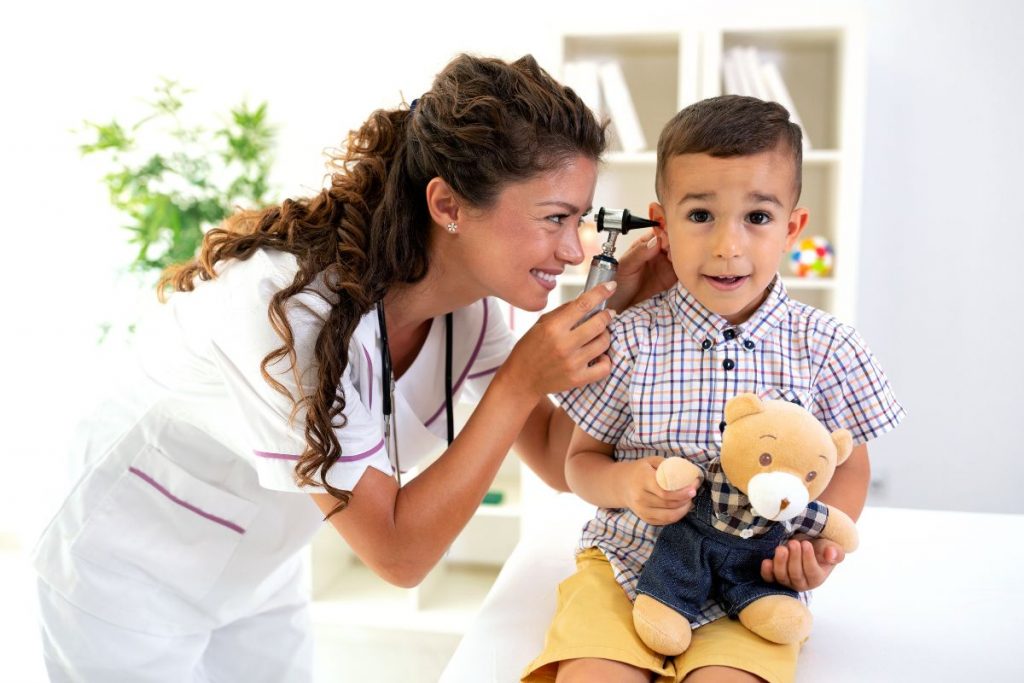
Diagnosing mastoiditis typically involves a clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional, who will review the patient’s medical history, assess symptoms, and perform a physical examination. The doctor may carefully examine the affected ear and surrounding areas for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, or tenderness. In some cases, imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the infection. CT scans can provide detailed images of the mastoid bone and help identify any abscesses or other complications.
Mastoiditis Treatment

The treatment of mastoiditis usually involves a multi-pronged approach that includes antibiotics, surgical intervention if necessary, and supportive care. Antibiotics are typically prescribed to target the underlying bacterial infection. The choice of antibiotics will depend on the severity of the infection, age of the patient, and the suspected or confirmed bacteria causing the infection.
In severe cases or when there is an abscess present, surgical drainage may be required to remove pus and relieve pressure on the mastoid bone. Pain management, such as over-the-counter pain medications or prescribed pain relief, may also be provided to alleviate discomfort. Supportive care, including rest, hydration, and proper ear hygiene, can also aid in the healing process.
Prevention of Mastoiditis
Taking steps to prevent middle ear infections, such as practicing good ear hygiene, avoiding smoking, and managing allergies or other predisposing conditions, can reduce the risk of developing mastoiditis. Prompt and appropriate treatment of middle ear infections, especially in high-risk populations such as young children and those with weakened immune systems, is crucial in preventing complications like mastoiditis. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional to effectively treat the infection and prevent recurrence. Regular check-ups with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may also be recommended for individuals prone to recurrent ear infections or other ear-related conditions.
Complications and Prognosis of Mastoiditis
When left untreated or inadequately managed, mastoiditis can lead to serious complications. The infection can spread to nearby structures, such as the brain, inner ear, or facial nerves, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions like meningitis, hearing loss, facial nerve paralysis, or sepsis. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, the prognosis for mastoiditis is generally favorable. Most cases of mastoiditis can be effectively managed with antibiotics and other supportive measures, and complications can be minimized or prevented with prompt medical intervention.
Importance of Timely Medical Intervention
Emphasize the importance of seeking prompt medical attention if one suspects mastoiditis or experiences symptoms such as severe ear pain, fever, or drainage from the ear. Delaying or avoiding medical care can increase the risk of complications and lead to more severe consequences. Stress the importance of following the prescribed treatment plan, completing the full course of antibiotics, and maintaining good ear hygiene to prevent recurrent infections.
FAQ
Mastoiditis is typically not associated with cancer. It is an inflammatory condition caused by bacterial infection of the mastoid bone. However, in rare cases, if there is an underlying malignancy (cancer) in the mastoid bone or adjacent structures, it may present with similar symptoms as mastoiditis. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis if there are concerns about cancer or any other serious medical condition.
Mastoiditis can occur at any age, but it is more commonly seen in children, especially those under the age of 2 years. This is because the anatomy of the ear in young children makes them more susceptible to middle ear infections, which can sometimes progress to mastoiditis. However, mastoiditis can also occur in adolescents and adults, albeit less commonly.
Various factors can increase the risk of developing mastoiditis. These may include a history of recurrent ear infections, especially untreated or poorly managed middle ear infections, compromised immune system, anatomical abnormalities or chronic conditions affecting the ear, such as cholesteatoma (a non-cancerous skin growth in the middle ear), previous ear surgeries, or trauma to the ear. Children under the age of 2 years are generally at higher risk due to their immature immune system and ear anatomy. However, mastoiditis can occur in individuals of any age, and other risk factors may also apply. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management of risk factors for mastoiditis.
Mastoiditis can be a serious condition if left untreated or if complications arise. In some cases, it can result in severe infections, abscesses, or spread of infection to nearby structures, such as the brain or inner ear. Timely and appropriate medical intervention is important to prevent complications and promote recovery.
Diagnosis of mastoiditis typically involves a clinical evaluation by a healthcare professional, who may take a detailed medical history, examine the ear, and assess symptoms. Imaging studies, such as CT scans, may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the infection.
Mastoiditis is generally not a condition that resolves on its own. It usually requires medical intervention, such as antibiotics to target the underlying bacterial infection, and may also require surgical drainage of pus or abscesses in more severe cases. Prompt and appropriate treatment is important to prevent complications and promote healing.
The presenting symptoms of mastoiditis can vary, but commonly include ear pain, fever, swelling behind the ear, redness or warmth over the mastoid area, drainage from the ear, hearing loss, and general discomfort. In severe cases, complications such as abscesses or other serious infections may also occur.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastoiditis is a serious condition that involves inflammation and infection of the mastoid bone, commonly associated with untreated middle ear infections. Understanding its definition, anatomy, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, complications, and prognosis is crucial for timely and effective management. If you suspect you or your loved ones may be experiencing symptoms of mastoiditis, it’s essential to consult a qualified healthcare professional, such as Dr. Shree C Rao, for proper evaluation and treatment.
Remember, early diagnosis and appropriate medical intervention can help prevent complications and promote a full recovery. Don’t delay, take action and seek professional medical advice to ensure the best possible outcome for your ear health. Schedule an appointment with Dr. Shree C Rao or your healthcare provider today. Your health and well-being are worth it!

Why consult EarSurgeon, Dr. Shree Rao?
Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is acclaimed as one of the best pediatric ENT specialists in Hyderabad. With 10+ years of deep domain experience in the field of ENT, she is the director at Dr. Rao’s ENT Super Specialty Hospital. She underwent specialized training in Rhinoplasty / Facial Plastic surgery at Singapore General Hospital, Singapore. She also underwent advanced training in cochlear implant surgery under Padmashri Dr. Milind V Kirtane and had a Fellowship in a cochlear implant. Having performed over 200 successful cochlear implants for patients worldwide, Dr. Shree Cuddapah Rao is also the recipient of several prestigious accolades in the domain of ENT. Dr. Shree Rao is one of the best ent doctor in hyderabad, to book an appointment click here.
Are you looking for
then you have landed at right place!